Saturday Feb 14, 2026
Saturday Feb 14, 2026
Wednesday, 16 July 2025 00:20 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}

Sri Lanka’s trade dynamics highlight both the promise of industrial expansion and the challenge of import dependency

After experiencing its most severe economic contraction in decades, Sri Lanka’s economy is gradually turning a corner. Between 2022 and 2023, the country underwent a painful but necessary period of adjustment following a debt-fuelled crisis. The latest projections for 2024–2027 suggest a modest but sustained recovery, with signs of improving investor confidence, rising consumption, and renewed capital formation.
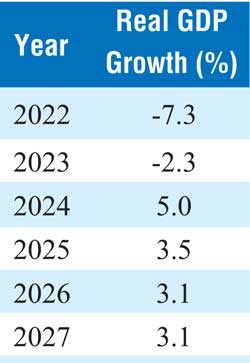
In 2022, Sri Lanka’s economy contracted by 7.3%, marking the peak of its financial crisis—triggered by unsustainable external debt, a collapse in foreign reserves, and severe governance failures. The impact was widespread, affecting households, businesses, and Government operations alike. Although the contraction moderated to -2.3% in 2023, the economy remained in a fragile state, with private consumption and investment still subdued.
The economy is forecast to rebound strongly in 2024 with real GDP growth of 5.0%, before settling into a more moderate pace of 3.1–3.5% annually from 2025 onward.
GDP growth
The sharp recovery projected for 2024 reflects base effects and a normalisation of economic activity post-crisis. Beyond 2025, growth is expected to stabilise.
Export and import trends
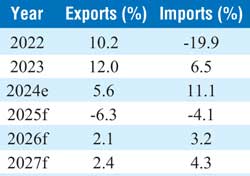
After a strong rebound in 2022 and 2023, exports of goods and services are expected to moderate to 5.6% in 2024, before contracting slightly in 2025. Imports, which dropped sharply in 2022, are forecast to rebound by 11.1% in 2024, potentially putting pressure on the trade balance.
 Import composition
Import composition
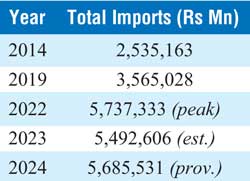
Sri Lanka’s total imports have followed a steep upward trajectory over the past decade. From Rs. 2.54 trillion in 2014, imports more than doubled to Rs. 5.74 trillion by 2022. Although 2023 saw a slight decline, provisional figures for 2024 indicate a rebound to Rs. 5.69 trillion.
The post-2020 surge is largely attributed to:
Currency depreciation
Global commodity price hikes
Post-pandemic demand recovery
Import trends by category
Food and live animals
2014: Rs. 290.2 b → 2024:
Rs. 721.7 b
Despite being an agricultural country, Sri Lanka increasingly relies on food imports—particularly cereals, dairy, and processed items. Rising food imports highlight a gap in local agricultural productivity.
Beverages and tobacco
2014: Rs. 15.2 b → 2024:
Rs. 37.0 b
Steady growth, driven by premium alcohol, branded tobacco, and shifting consumer preferences.
Crude materials (excluding fuel)
2014: Rs. 52.1 b → 2024:
Rs. 138.2 b
 Reflects rising industrial demand for timber, ores, and non-food agricultural inputs.
Reflects rising industrial demand for timber, ores, and non-food agricultural inputs.
Mineral fuels and lubricants
2014: Rs. 600.2 b → 2022:
Rs. 1.55 t (peak) → 2024:
Rs. 1.32 t
One of the most volatile categories. Heavy reliance on imported fuel exposes Sri Lanka to global oil price shocks.
Animal and vegetable oils, fats, and waxes
2014: Rs. 20.2 b → 2024:
Rs. 85.9 b
Growth driven by rising edible oil prices, especially during 2021–2022.
Chemicals and related products
2014: Rs. 269.3 b → 2024:
Rs. 702.7 b
 Increased demand for fertilisers, pharmaceuticals, and industrial inputs highlights critical external dependencies.
Increased demand for fertilisers, pharmaceuticals, and industrial inputs highlights critical external dependencies.
Manufactured goods (by material)
2014: Rs. 643.1 b → 2024:
Rs. 1.54 t
Includes imports of steel, rubber, plastics, and cement—key for construction and industry.
Machinery and transport equipment
2014: Rs. 523.6 b → 2024:
Rs. 876.8 b
A proxy for capital investment and infrastructure development.
Miscellaneous manufactured articles
2014: Rs. 116.9 b → 2024:
Rs. 262.0 b
Reflects changes in consumer behaviour and rising demand for electronics, apparel, and household goods.
Other/Not classified elsewhere
Remains marginal at less than Rs. 5 billion annually—includes diplomatic goods and special transactions.
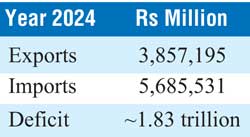
Trade balance
Sri Lanka’s trade deficit is structural, not cyclical—driven by essential imports such as fuel, machinery, food, and chemicals.
Policy recommendations
Strengths:
High capital imports reflect development momentum.
Broad import base supports multi-sector growth.
Concerns:
Rising food and fuel bills put pressure on foreign reserves.
Persistent trade deficits risk external sector instability.
 Strategic path forward:
Strategic path forward:
1. Accelerate renewable energy
→ Reduce oil dependency via solar, wind, and hydro expansion.
2. Boost agricultural self-sufficiency
→ Prioritise local production of cereals, dairy, and oilseeds.
3. Localise fertiliser and agro-chemical production
→ Enhance input security and reduce external dependence.
4. Promote import substitution
→ Focus on domestic production of packaging, plastics, processed food.
5. Export diversification
→ Expand non-traditional exports to reduce trade pressure.
Export composition highlights
Top performers: Tea, coconut, spices, garments, petroleum re-exports
Emerging sectors: Machinery components, chemicals
Risks: High concentration in garments; vulnerable to global demand shocks
Export policy suggestions
1. Climb the manufacturing value chain
→ Invest in electronics, green technologies, and engineering.
2. Enhance agro export branding
→ Position Sri Lankan tea, spices, and coconut as global premium brands.
3. Support SME exporters in regions
→ Empower SMEs in Eastern and Northern provinces for balanced growth.
4. Diversify export markets
→ Expand into ASEAN, Middle Eastern, and African markets.
5. Invest in R&D and industrial clusters
→ Especially in chemicals, machinery, and agri-tech sectors.
Conclusion
Sri Lanka’s trade dynamics highlight both the promise of industrial expansion and the challenge of import dependency. To ensure sustainable recovery and long-term economic stability, the
country must:
Strengthen domestic production in import-heavy sectors
Enhance export resilience through value-added goods
Tackle structural trade imbalances with innovation, energy transition, and smart trade policy
With disciplined reform and strategic investment, Sri Lanka can chart a more balanced and resilient economic future.
(The writer is a researcher in the legislative sector, specialising in policy analysis and economic research. He is currently pursuing a PhD in Economics at the University of Colombo, with a research focus on governance, development, and sustainable growth. He holds a Bachelor of Arts in Economics (Honours) from the University of Jaffna and a Master’s degree in Economics from the University of Colombo. His academic background is further strengthened by postgraduate diplomas in Education from the Open University of Sri Lanka and in Monitoring and Evaluation from the University of Sri Jayewardenepura. In addition to his research work, Muralithas has contributed to academia by teaching economics at the University of Colombo and the Institute of Bankers of Sri Lanka (IBSL), and has also gained industry experience as an investment advisor at a stock brokerage firm affiliated with the Colombo Stock Exchange. He can be reached at [email protected].)