Sunday Feb 22, 2026
Sunday Feb 22, 2026
Monday, 3 September 2018 00:00 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 Prime Minister of Sri Lanka, Office of the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka
Prime Minister of Sri Lanka, Office of the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka
www.wef.org: This is an important moment in Sri Lanka’s development, as the country continues to deliver on its plans for economic development and stands on the cusp of a transition to a knowledge-based economy.
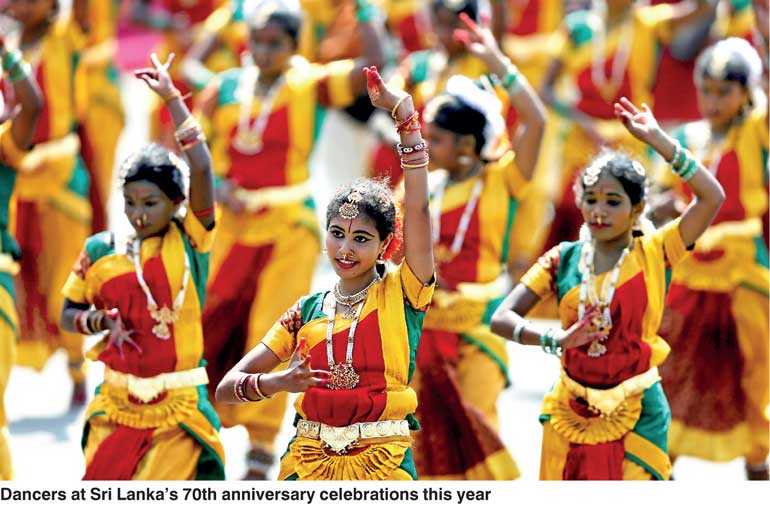
Since the country and its people saw a vibrant transition in its political landscape in January 2015, further bolstered by the August 2015 general elections that formed a national unity government – a first ever political experience for the country since its nearly seven decades of independence – Sri Lanka has put in place many of the building blocks needed to reinvigorate its socio-economic and political architecture.
We have achieved many positive gains over the last three years through bold policy initiatives and pragmatic strategies, that enabled the country to win back recognition and friendly engagements with the rest of world. This has been a key foreign policy achievement of our government. Doors are open again for constructive and friendly engagements that have eased economic and political pressures. However, as per the expectations of all our people, there is more to achieve and the government plans with due diligence to make Sri Lanka regain its centrality in the Indian Ocean and become a knowledge-based, highly competitive hub with a dynamic social-market economy.
The progress Sri Lanka has delivered over the past three years, and the success of its plans going forward, are naturally influenced by the global economic downfall and heavily tied to strategic trade relationships, in particular trade relationships across the Asian region. It is no secret that Asia is the future “economic engine”, and in our endeavours to make Sri Lanka a rich country by 2025, it is our intention to “engage Asia” more steadily, utilizing the strategic access to major growing markets in the region, from India, Pakistan, China, Japan and ROK to the ASEAN. Developments in Africa are also important in looking to South-South engagements and cooperation. While we undertake this re-orientation, we also continue to strengthen our partnerships with the West – particularly our top export markets of the United States and Europe.

Our economic policy, Vision 2025, is firmly embedded in several principles, including a social market economy that delivers economic dividends to all. In the first place we need to ensure we have a skill pool that matches the job market’s demands. Sri Lanka’s education system is being transformed through progressive and important policy reform: the minimum length of schooling has been increased to 13 years, while better education is being brought to rural areas through the Nearest School Is the Best School programme, and Sri Lanka is investing in more teachers and better training. Also, opportunities for vocational training in selected areas during school education will be introduced. Further, we have taken action to empower new and innovative ideas by strengthening the intellectual property regime in Sri Lanka. The plan for an “Empowered Sri Lanka” identifies the priorities of raising incomes, ensuring employment and housing for all, and improving the quality of life for all citizens.
The plan is delivering impressive results. The current government has created over 460,000 jobs and helped more than 260,000 families secure a home. Strong progress is being made on plans to bring opportunities to rural communities by building necessary infrastructure such as roads and bridges, connecting rural and urban areas and linking Sri Lanka’s economic hubs. A programme, Enterprise Sri Lanka, has been launched to encourage young and educated entrepreneurs, who will receive loans to start SMEs. The government has also invested in some mega projects, including the Colombo Megapolis constructions – to build a city of the future – and irrigation projects including the Moragahakanda-Kaluganga Dam, to generate green energy and provide water resources for agro-production.
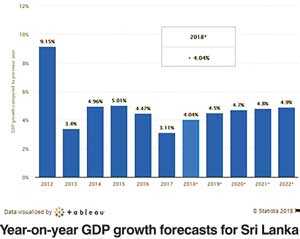
With a domestic market of 20 million consumers with a modest per capita income, Sri Lanka recognises the importance of external demand for sustained, high and long-term growth. This is why the country is rolling out a plan to strategically position Sri Lanka as the hub of the Indian Ocean, securing opportunities for local businesses in global production networks and ensuring that the country is capitalizing on opportunities to enter new global value chains. This outward-looking approach will increase the efficiency of the domestic economy, contributing to a better life for all Sri Lankans.
Sri Lanka is mindful of the shortcomings in its macroeconomic policies and institutional capacities that are required to respond to the challenges. We have encouraged strong public-private partnerships, and enabled institutions to become more transparent and efficient. We want them to function with independence, while ensuring transparency through being in compliance with norms set by the parliamentary oversight committees. The drive to end corruption is strong. We have enacted policy and legislative changes to facilitate doing business with Sri Lanka – it now ranks second in South Asia, according to the World Bank.
We have also played a constructive role in promoting international and regional initiatives in many areas, ranging from the environment and climate change to maritime security and migration. It is our commitment to use the strategic potential of the country, including its vibrant maritime connectivity, for enhancing friendly cooperation with all partners while reaping the economic benefits for all our peoples.
For the first time, Sri Lanka has now been linked to the large ASEAN region by entering into the free trade agreement (FTA) with Singapore. To have struck its first comprehensive trade agreement (including not only goods but services and investment) with a country like Singapore, regarded as one of the most open economies, with high-quality institutions, is an important milestone for Sri Lanka, and a major achievement for the current government. The Singapore FTA is a strong step towards closer integration with ASEAN, and in fact was signed in the same month that Singapore took over the chairmanship of ASEAN for the year 2018. It signals to ASEAN that Sri Lanka is interested in the region, and signals to the world that it is serious about reform.
The investment and trade resulting from the Singapore FTA is expected to drive the earning potential of Sri Lankans. Having created hundreds of thousands of jobs, the government is now focused on turning these into better paying jobs for people, in particular for youth and the younger demographics. The government has been clear that FTAs like this one are about opportunity, development and delivering a better standard of living for our people.
Sri Lanka has already begun preliminary discussions with another ASEAN country – Thailand – on a potential FTA, and formal talks were launched during the visit of the Thai prime minister to Colombo in July. This too is an important milestone, with Thailand taking over the ASEAN chair next year.
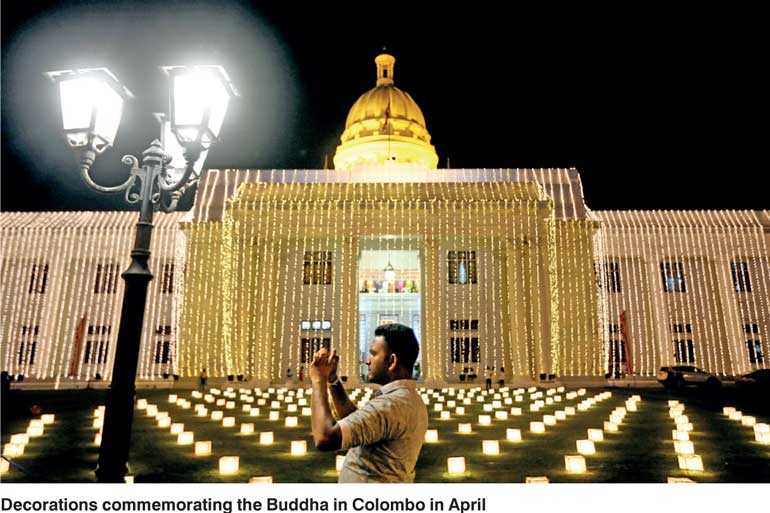

At present, Sri Lanka has “dialogue partner” status in ASEAN, as a member of the ASEAN Regional Forum along with 26 other countries. But the country will be using its trade agreements with Singapore and potential trade agreement with Thailand to bring it closer to obtaining observer status in ASEAN, with the goal of an FTA, as well as linking to the RCEP – the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership agreement.
We have also played a constructive role in promoting international and regional initiatives in many areas, ranging from the environment and climate change to maritime security and migration. It is our commitment to use the strategic potential of the country, including its vibrant maritime connectivity, for enhancing friendly cooperation with all partners while reaping the economic benefits for all our peoples.
For the first time, Sri Lanka has now been linked to the large ASEAN region by entering into the free trade agreement (FTA) with Singapore. To have struck its first comprehensive trade agreement (including not only goods but services and investment) with a country like Singapore, regarded as one of the most open economies, with high-quality institutions, is an important milestone for Sri Lanka, and a major achievement for the current government. The Singapore FTA is a strong step towards closer integration with ASEAN, and in fact was signed in the same month that Singapore took over the chairmanship of ASEAN for the year 2018. It signals to ASEAN that Sri Lanka is interested in the region, and signals to the world that it is serious about reform.
The investment and trade resulting from the Singapore FTA is expected to drive the earning potential of Sri Lankans. Having created hundreds of thousands of jobs, the government is now focused on turning these into better paying jobs for people, in particular for youth and the younger demographics. The government has been clear that FTAs like this one are about opportunity, development and delivering a better standard of living for our people.
Sri Lanka has already begun preliminary discussions with another ASEAN country – Thailand – on a potential FTA, and formal talks were launched during the visit of the Thai prime minister to Colombo in July. This too is an important milestone, with Thailand taking over the ASEAN chair next year.
At present, Sri Lanka has “dialogue partner” status in ASEAN, as a member of the ASEAN Regional Forum along with 26 other countries. But the country will be using its trade agreements with Singapore and potential trade agreement with Thailand to bring it closer to obtaining observer status in ASEAN, with the goal of an FTA, as well as linking to the RCEP – the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership agreement. (This article is part of the World Economic Forum on ASEAN. Source: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/08/this-is-how-we-will-make-sri-lanka-rich-by-2025/)
