Thursday Feb 19, 2026
Thursday Feb 19, 2026
Thursday, 25 April 2019 00:00 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}

By Eng. Col. Nissanka N. Wijeratne
The recent power crisis we encountered should not be a surprise to anyone as it was waiting to happen and of our own creation. When I say our own creation, it should be qualified, as it was not created by the ordinary citizens but by the political leaders in power, the power sector administrators, CEB and PUCSL. They are responsible for not taking timely decisions to add power generation plants to meet the increasing power demand.
The common excuse that heavy debt repayments is draining the Government revenue, leaving little room for capital investment, is not relevant as there are enough investors willing to setup power plants on PPP basis and supply electricity at rates cheaper than even the cost of production at Norochcholai, which stands at Rs. 18 per KWh when repayment of capital cost amounting to $ 1.35 billion is considered.
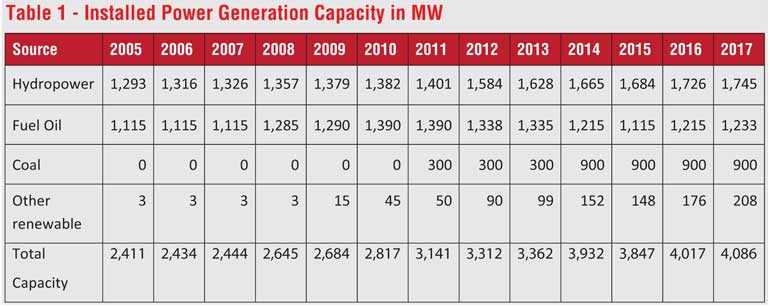
From Table 1 it will be seen that since the commissioning of the Final Stage of Norochcholai Coal Power Plant in 2014, no major power plant was added to the national grid. The total installed capacity of power generation that stood at 3932 MW in 2014 has increased to only 4086 MW by end of 2017. This is an increase of only 154 MW over three years. Even during 2018 no appreciable generation capacity was added. As per the Ministry of Power and Renewable Energy the power demand is estimated to increase by 6% annually. This means the power generation capacity should be increased at least by 200 MW annually.
However, it is quite possible that the assumed 6% annual increase in electricity demand could be surpassed with the GDP growth which will be accompanied with more industrial development, hotel construction, office and apartment buildings and most importantly improved lifestyles of people. A comparison given in Table 2 indicates that the per capita electricity consumption in Sri Lanka is still lower than in the other Asian countries with similar climatic conditions when correlated to the per capita GDP.
It is seen that India with per capita GDP of $ 1,942.1 has per capita electricity consumption of 1122 KWh whereas Vietnam with per capita GDP of $ 2,342.2 has per capita electricity consumption of 1312 KWh. Both these countries have lesser per capita GDP but much higher electricity consumption than us. With per capita GDP of $ 4,073.7 our electricity consumption is 494 KWh.
When planning our future electricity demand, considering our relatively higher per capita GDP, it may be safer to assume the electricity consumption to reach at least 1000 KWh per capita in the near future. When it happens the power generation capacity should be needed to double. This means additional 4000 MW! Constructing power plants with installed capacity of 4000 MW will require a capital investment of minimum $ 4 billion.
It would be most prudent to attract investments to setup these power plants on BOO basis with no capital investment by the Government. The only involvement of the Government should be to lease suitable lands and providing power purchase agreements, both for 25-30 years. For private investment on large power plants (over 25 MW) a major obstacle is the Section 9(c) of the Sri Lanka Electricity Act, No. 20 of 2009. As per this Section only a company incorporated in Sri Lanka in which;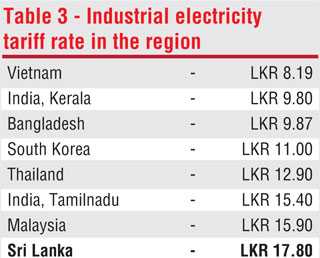
a) Government, a Public Corporation, a Company with more than 50% shares held by Government or a Company with a Government subsidiary holding majority shares, holds the number of shares determined by the Secretary to Treasury with the concurrence of Minister of Finance, can undertake a power generation plant exceeding 25MW.
If the intention is to facilitate private investment in power generation this Section with above restrictions should be suitable amended. As Sri Lanka is not the only destination for investments and other countries not having such restrictions, it is no wonder that to date there is not a single major power plant constructed by a private investor.
As such the Section 9(c) should be amended to allow any company incorporated in Sri Lanka and issued a generation license by PUCSL with the approval of the Government to undertake a power generation plant exceeding 25MW. With a favourable legal framework and a healthy investment climate there will be absolutely no difficulty in attracting investments for power generation with a lease of land and power purchase agreement.
The proposal made by Energy World International Ltd., which is a British-owned company based in Hong Kong, can be cited as the best example for a private investment on a power generation plant of capacity 1200 MW in four stages of 300 MW each at Hambantota Port.
This proposal was submitted in response to a RFP, published in newspapers, maritime magazines, SLPA website, etc. giving wide publicity in July-August 2012 inviting investments for industrial ventures at Hambantota Port. It was one of the 10 proposals received at the tender opening on 27 September 2012 by the CANC. After a detailed evaluation by the PC & CANC, which even went to the extent of checking financial credibility through an international accounting firm, five proposals were selected to recommend for implementation.
Constructing a LNG hub terminal comprising of loading/unloading facility with 80,000 cm storage tank and combined cycle LNG power station with total capacity of 1200 MW in four stages of 300 MW each at two year intervals over a period of eight years with a total investment of $ 1,350 million was one of these proposals selected.
As per this proposal SLPA will have to lease 30 Ha of land at Hambantota Port for 25 years. The investor will pay $ 1.5 million annually, increased by 3% every year for the land. CEB had to enter into a Power Purchase Agreement for 25 years. The initial rate offered was $ 0.09 (US cents 9) per KWh, later reduced to $ 0.07 (US cents 7 during negotiations. The investor did not insist on a capacity charge or any other charges. This rate of US Cents 07 means that electricity from this plant will be available at Rs. 12.36 per KWh, cheaper than the rate of Rs. 18 at Norochcholai.
The CANC report was first considered by the Cabinet of Ministers on 03-04-2014, at which it was decided to direct the Secretary to Ministry of Highways, Ports and Shipping to further discuss the proposal considering the various observations received from other Ministers with Secretaries to the Ministry of Finance and Planning, Power and Energy and Investment Promotion and submit a report.
On 30-10-2014 the Cabinet of Ministers considered the CANC report, the report submitted by Secretary to Ministry of Highways, Ports and Shipping prepared in consultation with the other Secretaries and observations received from different Ministers and decided to accept the proposal of Energy World International Ltd. of Hong Kong to establish a LNG hub terminal and combined cycle LNG power station with total capacity of 1200 MW in four stages of 300 MW each at two-year internals at Hambantota Port on a 30 Ha land leased for 25 years by SLPA, subject to following:
First 300 MW generation plant to be operational within two years of award, by end of 2016.
JV to be established with 10% shares issued to Secretary to the Treasury, for the value of the land leased, to comply with Section 9(c) of the Sri Lanka Electricity Act, No. 20 of 2009. Secretary to Treasury to have full controlling power on the business and its assets with a Golden share of 10% given for the lease of land.
BOI to enter into an agreement with the JV as a strategic investor.
Implementation Agreement and Land Lease Agreement to be entered between SLPA & JV.
Power Purchase Agreement to be entered between CEB & JV with an agreed pricing formula. The negotiated price to be between $ 0.065 – 0.07 (cents 6.5 to 7.0) per KWh with no capacity or other charges.
After the Cabinet Approval, SLPA issued a letter allocating 30 Ha of land. But when attempting to finalise JV agreement following problems cropped up. Naturally the JV could not be entered:-
If the investor has to issue 10% shares in the JV to Secretary to Treasury for the value of land leased, why should there be any annual lease payment to SLPA. SLPA wanted the lease payments.
Who is the investor with a sound mind that will allow full controlling power to Secretary to Treasury, after investing $ 1,350 million? The total freehold value of the land may not reach even $ 50 million. These requirements came due to the Section 9 (c) of Sri Lanka Electricity Act, No 20. of 2009.
Some salient features of this proposal are highlighted below:
The Energy World International Ltd. is a company formed by British nationals and based in Hong Kong. This company has majority shares in Energy World Corporation Ltd., which is a public company listed in Australian stock exchange. It has extensive experience on LNG storage transportation and power generation. It owns gas production wells in Australia and Indonesia.
The company had paid Rs. 9.0 million as processing fees to BOI.
This Company also planned to export LNG and to supply for any domestic requirements. Another objective was to supply compressed natural gas (CNG) for heavy transport vehicles and ships.
The company will guarantee uninterrupted power supply from its generation plant, reserving only 50 MW for any maintenance at any given time. This means with first 300 MW installed in two years we will have guaranteed uninterrupted supply of 250 MW. With the 2nd stage this will increase to 550 MW. On failure to supply uninterrupted power investor will compensate for any losses. This is a huge advantage when the bad experience with numerous failures at Norochcholai plant is considered.
The Government or CEB will have no burden on arranging the supply of LNG. Procuring LNG in international market for a single power plant could pose problems, with big players securing their supplies on long term basis.
Total investment will be transferred from abroad and nothing raised from local banks.
The cost of electricity from this plant at 7.0 US Cents will be Rs. 12.36 per KWh at the present exchange rate ($ 1 = Rs. 176.50). Cost of power generation from diesel plants is Rs. 30-32 per KWh. At Norochcholai it is Rs. 18 per KWh. With the introduction of 300 MW of LNG plant from this investor, the annual serving will be to the tune of Rs. 40 billion by not resorting to diesel generators.
This investor was willing to supply LNG for conversion of 300 MW existing thermal combined cycle power plant at Kerawalapitiya at a competitive rate. This would have generated further savings to CEB.
LNG is considered green energy unlike coal. In many countries now coal power plants are being either shut down or new coal power plants not started.
However, due to a change of policy by the Government, on 21 June 2016 the company was informed by SLPA that all the projects at Hambantota Port were suspended on a decision of CCEM. Subsequently, the Government entered into negotiations with China to handover the Hambantota Port on a long lease to settle the loan taken for constructing the Port. But the grave mistake committed by the Government was to abandon the good projects already negotiated for the Hambantota Port such as the LNG power project.
If this project was included in the negotiation with the Chinese, most probably they would have agreed to accommodate, as the Energy World International Ltd., is a company based in Hong Kong and China Harbour Co. also has a strong presence in Hong Kong. Alternatively, the Government could have relocated this LNG project at Trincomalee Harbour, as the Sampur Coal Power Plant was also cancelled. Had it been implemented in 2015, by now CEB should be drawing from the 1st 300 MW plant and there would have been no reason for the power cuts.
But the real reason for good investment projects not proceeding, could be due to the fact that most international companies formed by British and EU nationals are reluctant to pay large commissions to win contracts. It was the same story with a leading Norwegian company on producing electricity from garbage, who was very keen in 2013 to scientifically manage the garbage dump at Meethotamulla to produce electricity. Had he been able to proceed, the Meethotamulla disaster would not have happened. Then there was the British investor interested in producing microchips at Hambantota. Both companies got fed up.
Apart from the LNG power project mentioned above cancelation or indecision on many other projects has led to the present power crisis. These are:
Cancellation of Sampur coal power plant. If coal is environmentally not acceptable, why was a LNG plant not established?
Delay in finalising the investment proposal to establish a 300 MW combined cycle plant at Kerawalapitiya which was tendered in November 2016. Manipulating the tender procedure not to award the contract to Lakdhanavi Ltd. which was ranked No. 1 by TEC four times and recommended by SCAPC in March 2018, on a decision by the PAB will further delay this project as it has gone to the courts now. Lakdhanavi Ltd. has offered to sell electricity at Rs. 14.98/KWh whereas the GCL, Windforce & RenevGen, the company favoured by the powers be, at Rs. 15.97/KWh. This will result in an extra cost to CEB of Rs. 2,125 million annually for 20 years, totalling Rs. 42,495 million. Who will bear this extra cost? It is the consumers, to fatten the purses of few decision makers. Even if this power plant is established how can it be operated on LNG without an arrangement to supply LNG?
The current proposal being considered to supply LNG through a Korean company could be another disaster in waiting as the commitment needed to buy a large quantity of LNG will be much beyond the requirements of our country. The most prudent proposal would have been to find an investor to put up a LNG power plant with LNG supply arrangement similar to the proposal submitted by Energy World International Ltd.
Delay in converting the existing 300 MW thermal power plant at Kerawalapitiya to use LNG which will result in huge savings.
In summary, the power crisis is created by the politicians, administrators, CEB and PUCSL by not taking the correct decisions in time causing huge damage to our motherland. Because of these selfish acts, our industrial electricity tariff rate is the highest in the region as seen from Table 3.
With the above, can we hope for rapid industrial development to create employment?
(The writer is Secretary General/CEO, Chamber of Construction Industry Sri Lanka.)