Wednesday Feb 18, 2026
Wednesday Feb 18, 2026
Tuesday, 21 December 2021 00:51 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}

Neo banks are now taking the lead in financial intermediation in a different mode offering affordable financial services to a broader segment of the population hitherto underserved by the traditional banks and other financial services providers
 Managing Sri Lanka’s finances in the current post-pandemic economic conditions has become challenging, and the foreign exchange reserves are rapidly depleting. The finance minister is negotiating swap deals to manage the cash flow. The glaring mismatch between the country’s revenue and expenditure, be it local or foreign, is the crux of the problem.
Managing Sri Lanka’s finances in the current post-pandemic economic conditions has become challenging, and the foreign exchange reserves are rapidly depleting. The finance minister is negotiating swap deals to manage the cash flow. The glaring mismatch between the country’s revenue and expenditure, be it local or foreign, is the crux of the problem.
For decades we have been facilitating a debt infused growth, assuming the foreign exchange inflow from the migrant workforce and the incoming tourist to remain constant. Debt induced growth scenario is similar to prolonging a terminally ill patient sustaining a saline drip. With all the unconventional monetary policy tools, the current economic conditions are doubtful to trigger substantial economic growth to weigh the accumulating debt levels across the globe, particularly in Sri Lanka.
Furthermore, overheating economies elsewhere are compelled to move soon away from the zero or negative interest rate policies. In such a scenario, highly indebted countries like Sri Lanka will face further trouble borrowing money from international markets. Moreover, current debt servicing will worsen our finances.
The Government encourages the exporters to convert their foreign exchange earnings by keeping the convert at an artificially low exchange rate. Market rates and information are freely available in the current era of acceleration with the help of the internet and all the smart digital tools. Traditional monetary policy tools used by the central banks through commercial banks by exchange rate manoeuvring will not work as in the past as the alternative finances are increasingly offering new financial services on the latest digital platforms. The current regulatory architecture designed during the analogue era may find it difficult to effectively function in this digital era.
In light of the development mentioned above, this article highlights how the neo banks and alternative finances are gearing up to compete in the traditional financial services industry.
What are the neo banks and alternative finance
This paper consists of excerpts of a conference paper on Neo Banks and Alternative Finance written for the Sixth UNI Asia and Pacific Regional Organization Finance Sector Conference held on 22 and 23 November. Neo banks are now taking the lead in financial intermediation in a different mode offering affordable financial services to a broader segment of the population hitherto underserved by the traditional banks and other financial services providers. Therefore universal and commercial banks confront a new group of competitors. Entry barrier advantageous previously enjoyed by the banks are likely to disappear soon.
Neo banks are digital-only banks that don’t have physical branches or rely on legacy operating systems. Although many governments in Asia have already issued licenses to set up digital banks, the neo banks are promoted by the big tech companies such as Google, Apple, Facebook, and Amazon. These tech behemoths are offering innovative alternative financial services competing with traditional banks. Crowdfunding and Peer Peer (P2P) lending are few alternative finance platforms increasingly established in the markets.
The Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance (CCFA), attached to Cambridge University Judge Business School, initiated a pioneering online comprehensive study on the growth of alternative finance in 2018. This report presents the key findings from the CCAF annual global survey of alternative online finance. The study focused on Crowdfunding, P2P/marketplace lending and other capital raising activities of 2322 firm-level observations globally.
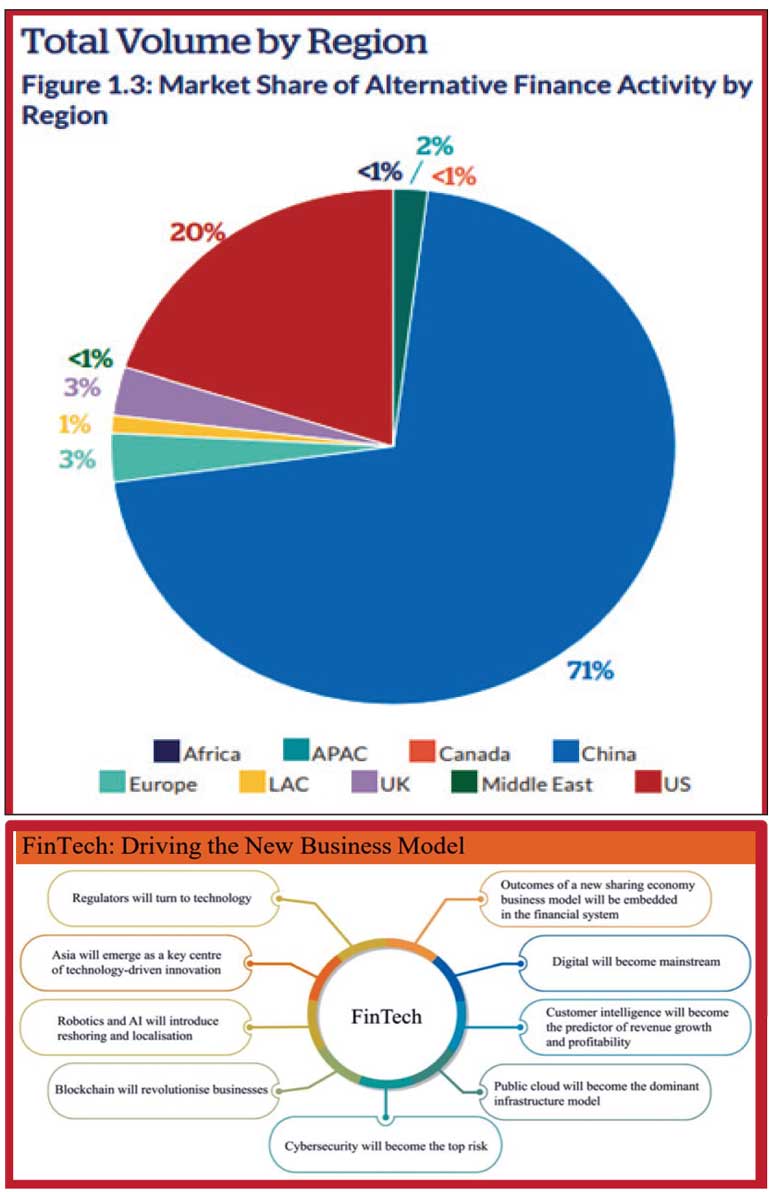
In 2018, the global alternative finance industry facilitated $ 304.5 billion in transaction volume. This global alternative finance volume represents funds raised via an online alternative finance platform for consumers, businesses, and other fundraisers.
Facts revealed in the study countries such as Australia, China, Japan, and Indonesia from Asia & Pacific have taken the lead in market share and volumes. These figures were as of 2018, but the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the process exponentially with the social distancing and subdued economic activities promoted on non-cash transactions.
Now the digital disruptions are part of the new normal. The banks are forced to think of new business models and strategic alliances with high tech companies who are coming up with new payment models circumventing the traditional banking systems.
Aside from the technologies above, smart phones are the critical handheld device that sets the pace of digitalisation. The new customer convenience is emerging with the evolving technology such as Video Banking, Chatbots, etc. COVID-19 pandemic led social distancing measures further stimulated the introduction of these services.
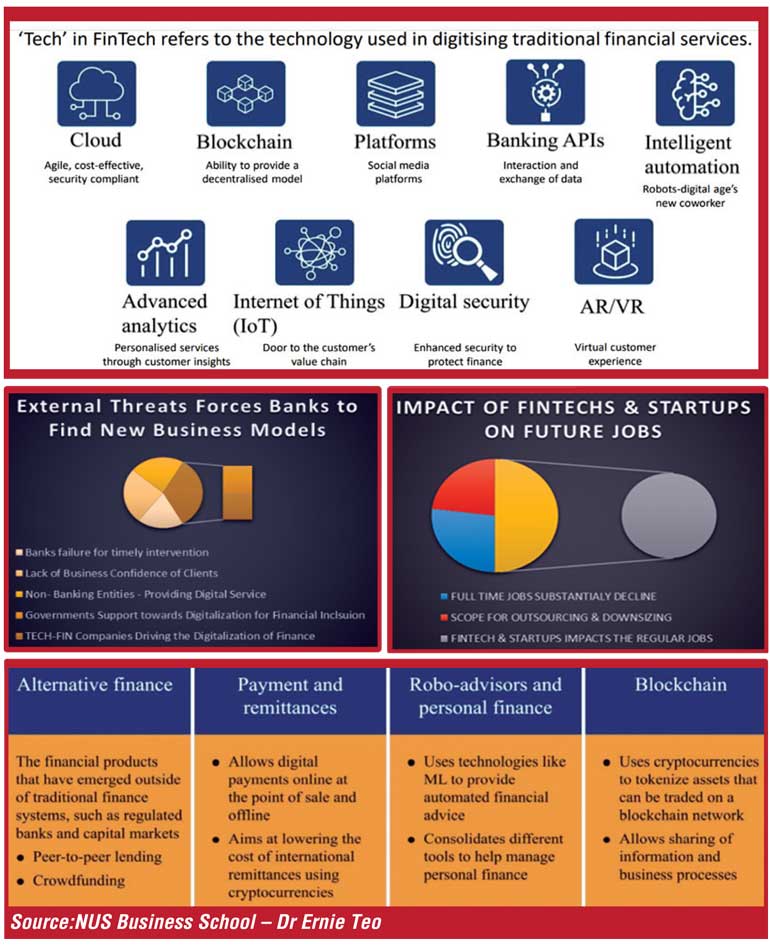
The banks have felt the challenges and building up strategic alliances with the tech companies providing various services developed on digital platforms. Banking sector unions in the Asia and Pacific confirmed this development responding to a survey initiated by UNI Apro Finance.
Three critical external threats ranked high in the survey. As shown in the above pie chart, it explains the threats from fintech and non-banking entities. In addition to the Government supports tech fins to widen financial inclusion through digitalisation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made investors anxious, or at least cautious, about an economy that is taking longer than expected to recover. According to Jakarta Post, there is no shortage of money going into start-ups and tech companies as venture capital bets on the megatrend of digitalisation. According to the Financial Services Authority (OJK), venture capital financing or placement in Indonesia has risen 24.86% year-on-year (YoY) to Rp 16 trillion ($ 1.11 billion) in June, almost matching the 25.47% YoY increase recorded in June 2020. (The Jakarta Post, 2021).
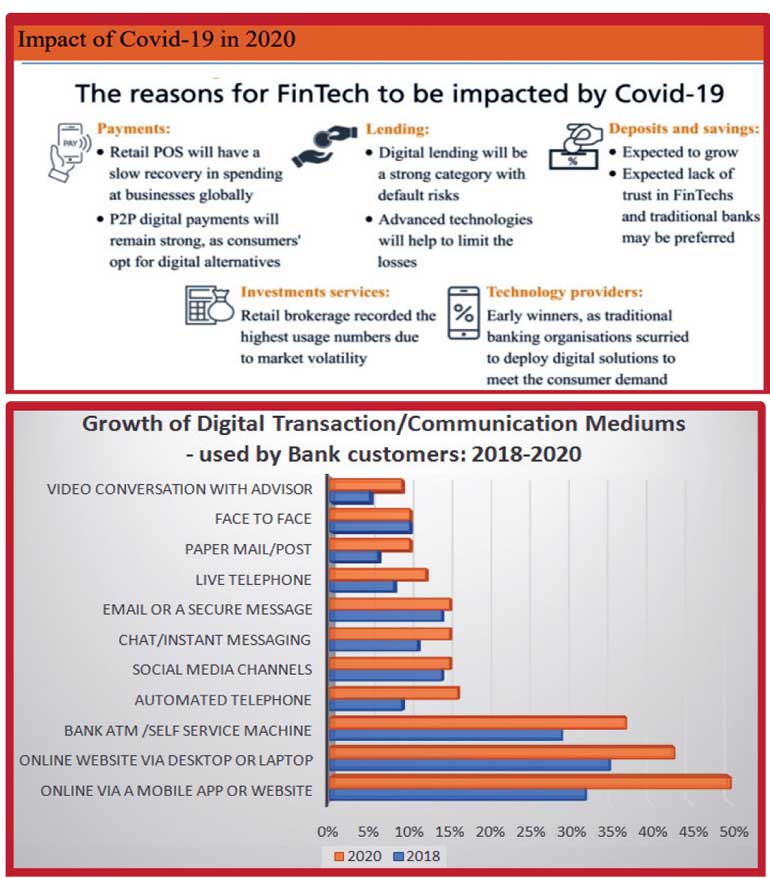
Customer preference digital financial services – Accenture study
Banking Consumer Study, conducted by Accenture’s; synthesises, the sudden increase in digital adoption is both a blessing and a curse for banks. The study was one of the largest and based on interviews with 47,000 banking customers in 28 markets. Accenture’s report further highlights, though the efficiency has dramatically advanced most banks’ digital agendas, the lack of human connection poses the risk of banks weakening their already tenuous personal and emotional connection with customers. The trend makes banking more commoditised and price-driven.
It hampers banks’ efforts to shore up customer trust – which has been waning for years and is critical to their ambition to grow revenue through personalised advisory services. The graph depicts the customer preferences and shifts towards digital transactions from pre-pandemic 2018 to 2020. (Accenture, 2021)
The sharing economy dominates the existing financial system. FinTech will be driving the new business models in every sector, including banking and financial services. Customer intelligence will be the most important predictor of revenue growth and profitability. In addition, blockchain evolving technology will shake up how businesses operate. as the world becomes more accepting of the sharing economy and decentralisation; blockchain will become the enabling technology. it will allow for payments to be in a decentralised manner.
Smartphones, cloud computing, AI and machine learning, the Internet of Things, blockchain, and cryptocurrencies will continue to play a significant role in every part of the financial system.
In the past, tech companies followed the finance industry to spot opportunities to offer digital solutions; we defined them as fintech. The tech companies have leapt forward, and now they lead and do not follow others; as such, the new definition applicable to them directly is Tech-Fins. They are creeping the following financial services contributed to the revenues of banks.
Alternative finance
The financial products that have emerged outside traditional finance are alternative finance. Peer 2 Peer Lending (P2P), crowdfunding is now gaining popularity. The given table enumerates the other types of alternative finance.
Role of Central Banks Digital Currencies (CBDC)
CBDC is different from virtual currency and cryptocurrencies. A central bank digital currency is issued using a database run by the central bank or government-approved private sector entities. A digital currency, like a CBDC, would allow anyone to hold money without having a bank account. CBDCs can also prevent illicit activities, help in tax collection, and combat crimes such as money laundering. It allows for the protection of money as a public utility to replace physical cash.
It also anxious safety of payment systems. Creates competition among banks and allows for the transmission of monetary policy. CBDC also ensures financial security for the country. It will limit the practice of fractional reserve banking. China is one of the first countries that announce a sovereign-state backed digital currency on a government level.
Upcoming trends and role of technology in the finance sector
Globally, about 1.7 billion adults remain unbanked. Virtually all these unbanked adults live in the developing world. Financial Services can help drive development, assisting people to escape poverty by facilitating investments in their health, education, and businesses. Many poor people around the world lack the financial services that they need.
Studies have shown that mobile money services, which allows users to store and transfer funds through a mobile phone, can help improve people’s income earning potential and thus reduce poverty. Kenya’s M-Pesa, mobile money banking enabled women-headed households to increase their savings by more than a fifth.
The unbanked can be reached with financial technologies: low margin, asset-light, scalable, innovative, and easy compliance. FinTech has been used to smooth out operation pain points to lower costs. And at the same time, data technology provides opportunities to create new services. Innovative digital financial services can also help people accumulate savings and increase spending on necessities. A well-developed payment system, good physical infrastructure, appropriate regulations, and robust consumer protection to save costs is necessary to bring in the benefits of fintech to the community. Whether it’s digital or analogue, financial services need to be tailored to the needs of disadvantaged people, such as women, poor people, and first-time users of financial services,
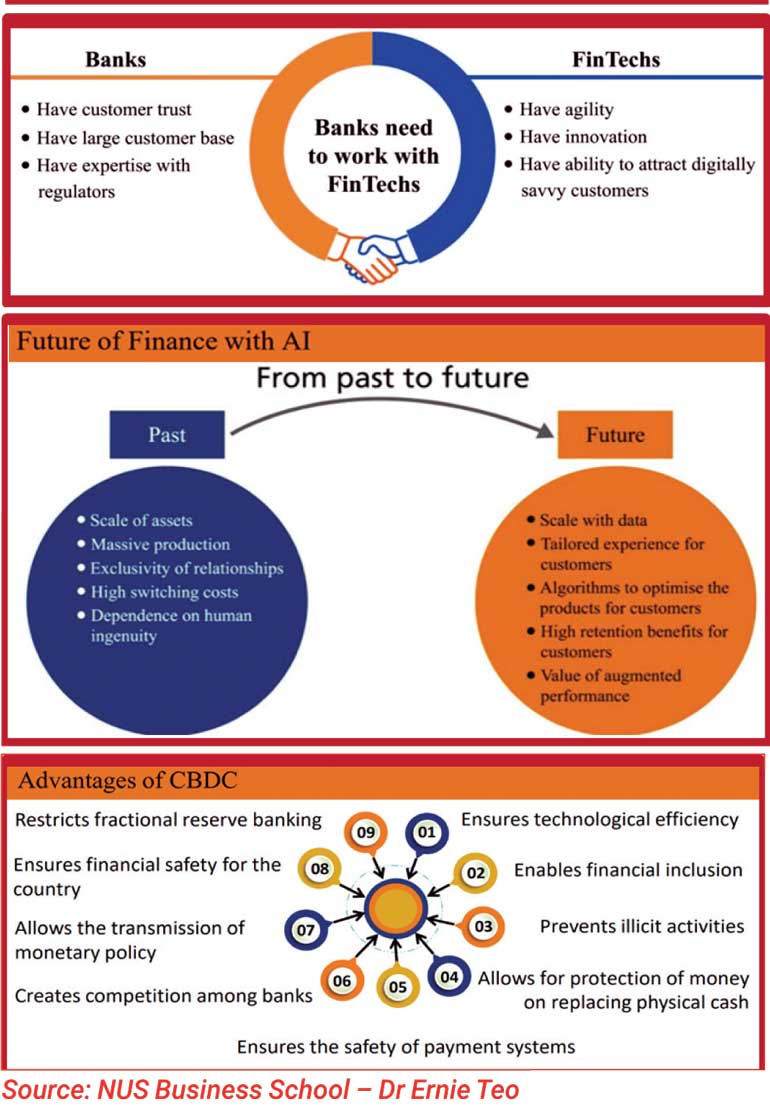
Role of AI reshaping finance sector
Bankers are likely to become AI agents in future. With the help of AI, self-driving bankers will offer customers guidance on complex decisions such as home buying or retirement planning or corporate financing. AI overwhelmingly helps banks to mobilise and scale data instead of assets. Everyone will get a different financial product based on their needs and data, enabling a tailored experience for every customer. AI algorithms optimise the products for customers and match the products to suit them. Moreover, augment the performance of financial services and provide value to customers through using AI and machine learning and big data and retaining the loyal customers in the banks.
AI and Machine learning capabilities will ease customer identification with facial recognition and biomatrix. Moreover, with data support and AI and ML technologies, banks can spot and identify profitable customer segments and effectively manage risks and market predictions. These technologies can address anti-money laundering and fraud processing issues and utilise them in chatbots and virtual agents. Furthermore, automating lending with the help of data analytics will undoubtedly improve customer services satisfactorily.
The way forward
Peer to peer lending, crowdfunding is a new alternative finance option they are gaining momentum. Internet is enabling all these services across geographies with minimum regulatory controls. Payment transfers and international remittances are following the same trend. If governments offer unattractive exchange rates, the digital natives will provide creative solutions to minimise the losses resulting from accumulating negative net worth in their balance sheets and help them tie over the cash flows.
Blockchain technology will be the next supernova similar to the internet; it can create a new financial architecture preventing the undue gains made by the existing financial intermediaries in the global capital markets.
The Sri Lankan financial experts and policymakers will analyse the new policy tools to address the crisis and the short-term issues. Analogue era policy tools are now part of history.
In doing this article, I acknowledge the academic contributions of Dr. Ernie Teo. Adjunct Senior Lecturer, National University of Singapore Business School. Dr. Teo is attached to the Department of Analytics and Operations at NUS Business School. The illustrative diagrams used in the article are of his creations, used for knowledge sharing purposes to benefit the readership.
(The writer is the Regional Director for Finance Sector Activities attached to UNI Asia and Pacific Regional Organization in Singapore. He can be reached at: [email protected].)