Tuesday Feb 17, 2026
Tuesday Feb 17, 2026
Wednesday, 15 November 2017 00:08 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
The majority of Sri Lankans invest their hard earned money in banks and finance companies in the form of fixed deposits and savings products. However, there are a number of other financial instruments available for investment for retail investors which includes the following:
1.Government securities
2.Listed debentures
3.Listed shares
4.Unit trusts
5.Insurance products
Below is a brief insight into each investment option and the risk factor:
1.Government securities
Government securities are debt instruments issued by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka on behalf of the Government  of Sri Lanka. Government securities are considered as the safest investment available for an investor. There are two types of government securities, namely treasury bills and treasury bonds. Treasury bills are short term securities with tenures of 91, 182 and 364 days. The treasury bonds consist of medium to long term government securities with tenures ranging from 2 years to 30 years. Treasury bills do not pay interest as they are issued at a discount to the face value while treasury bonds pay interest semi annually.
of Sri Lanka. Government securities are considered as the safest investment available for an investor. There are two types of government securities, namely treasury bills and treasury bonds. Treasury bills are short term securities with tenures of 91, 182 and 364 days. The treasury bonds consist of medium to long term government securities with tenures ranging from 2 years to 30 years. Treasury bills do not pay interest as they are issued at a discount to the face value while treasury bonds pay interest semi annually.
A retail investor could invest in a government security through a commercial bank or a primary dealer. Primary dealer is an intermediary appointed by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka who is engaged in buying and selling of government securities.
2.Listed debentures
Listed debentures are debt securities issued by business entities/corporates which are listed on the Colombo Stock Exchange. Corporates issue listed debentures to partly finance debt funding requirements. The major issuers of listed debentures in Sri Lanka are banks and finance companies. A retail investor could invest in listed debentures through a stock broker.
Listed debentures are riskier than investing in government securities and hence give a higher return relative to government securities. An investor can have an idea of the default risk of a listed debenture based on the credit rating of the debenture. All listed debentures have a mandatory credit rating which is published by an approved credit rating agency. Higher the credit rating of a listed debenture, lower the incremental risk compared to a government security. In contrast, lower rated debentures carry a higher level of incremental risk over the government securities.
3.Listed shares
Investing in listed shares is another investment option available to retail investors. Investing in shares involve taking an ownership stake in a business entity/corporate which entails risks associated with the business of the investee company. Hence, investing in listed shares carries the highest degree of risk (out of the investment options discussed in this article) and the investor is expected to have the required knowledge and expertise to analyse the investment prior to making investment decisions in listed shares. Listed shares have the potential to generate the highest return to an investor in the long run reflecting the highest level of risk associated. An investor can invest in listed shares through a stock broker.
 4.Unit Trust
4.Unit Trust
The three investment options discussed up to now, are direct investment instruments available to a retail investor. This requires investment management expertise and time from the part of the investor.
In contrast, unit trusts pool funds from a large number of investors and invest such pooled funds in different types of investment instruments. Unit trusts are managed by full time professional fund managers. Therefore, investing in unit trust is a convenient alternative for a retail investor who does not have the time and expertise to invest in first three types of investment instruments discussed above.
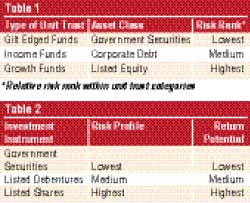
There are different types of unit trusts as tabulated in table 1 which have specialised in investing in government securities, corporate debt and listed shares.
The risk profile of a unit trust depends on the asset class in which it invests in. For example, a growth fund which invest in listed equity is riskier than a gilt edged fund which is exposed to government securities.
5.Insurance products
Life insurance companies offer different types of long term investment plans for retail investors. Such investment plans include savings plans, retirement plans, education plans for children, etc.
Conclusion
The summary of risk return profile of different types of investment instruments are given in the table 2.
Despite the availability of fairly a wide choice of alternative investment instruments, Sri Lankans pre-dominantly invest in fixed deposits and savings products of banks and finance companies. Lack of awareness, knowledge and poor access to intermediaries who distribute these products are the major deterrents for low level of penetration of these alternative investment instruments. With the development of technology which enables mobile lead distribution of financial services would certainly help in reaching the masses for these alternative investment instruments.
(The writer is a senior corporate finance and strategy consultant with over two decades of experience locally and internationally.)