Thursday Feb 19, 2026
Thursday Feb 19, 2026
Thursday, 20 September 2018 23:05 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
The tax regime in Sri Lanka historically imposes WHT on both domestic as well as cross border payments. WHT on domestic payments eases revenue collection (e.g.: PAYE) while WHT on cross border payments are adopted by most countries to ensure that the fair share of tax is retained in the host country.
As regards cross border payments, provisions of treaty override comes into effect if a Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (“DTA”) has been entered between the host and home country. Sri Lanka has over 44 DTA agreements with various treaty partners and the rates applicable in these Agreements tend to vary but generally reduced rates are afforded by same. 
In the absence of a DTA with the home country, WHT on cross border payments are imposed at the rates specified in the domestic statute. Taxation in Sri Lanka has been changed significantly with the new Inland Revenue Act No.24 of 2017 which is effective from 1 April 2018.
According to the charging section, income tax is imposed on a person – who has taxable income for that year as well as a person – who received final withholding payment during the yearFinal withholding payments
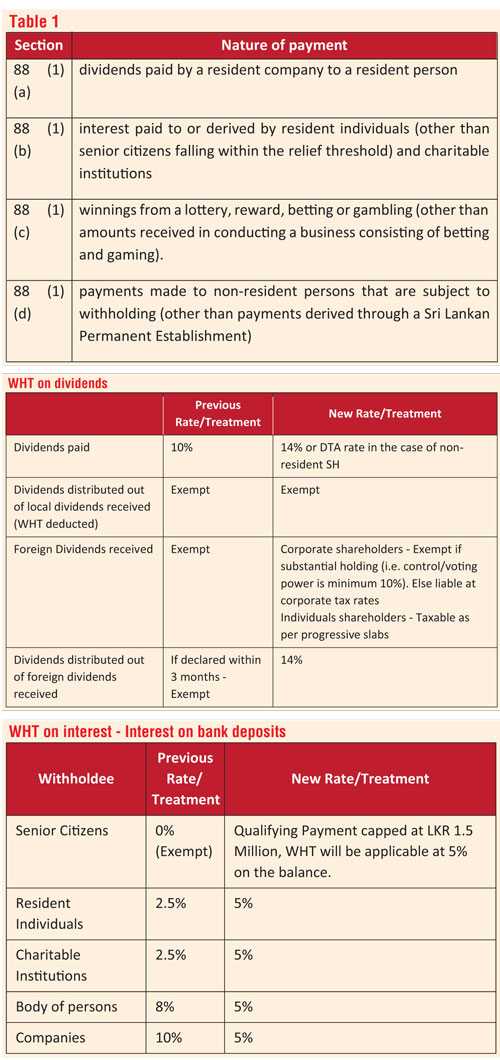
Taxes withheld under table 1 are considered to be final withholding payments and will not be subject to any further tax. The onus of withholding, sources and compliance measures are set out in Chapter VIII – Division II- (Tax Payable by withholding) while the rates are set out in the First Schedule of the Act. I have summarised it below for the reader’s convenience.
Employers are required to deduct WHT on employment income at rates specified by the Commissioner General and published in the Gazette dated 1 April 2018 bearing number 2064/60 and the tax rates have been issued by the IRD in its official site. Accordingly, employers are required to obtain a Primary Employment Declaration Form from employees where regular profits are in excess of Rs. 100,000 per month or Rs. 1,200,000 per year of assessment.
Previously PAYE tax is considered final in the hands of employees who do not have any other source of income. However, in the 2017 Act, employment income where WHT is deducted has not been included as a final tax. Nevertheless, as per Section 94 (1) (a) (ii) no return of income is to be furnished by an individual who has exclusively employment income that has been subject to WHT.
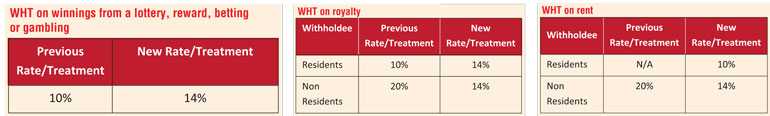
This section captures investment returns such as dividend, interest, discount, charge, natural resource payment, rent, royalty, premium or retirement payment or amounts received as winnings from a lottery, reward, betting or gambling.
2.3 Partnership share of income (Sec 84 (1) (ii))
 Unlike in the past, a partnership is not be liable to pay income tax on its Taxable Income instead a withholding tax of 8% will be deducted from relevant share of any partner’s income from the partnership.
Unlike in the past, a partnership is not be liable to pay income tax on its Taxable Income instead a withholding tax of 8% will be deducted from relevant share of any partner’s income from the partnership.
2.4 Sale of Gems at an auction (Sec 84 (2))
The National Gem and Jewellery Authority established by the National Gem and Jewellery Authority Act, No. 50 of 1993 is supposed to withhold tax at 2.5% from the sale price of any gem sold at an auction conducted by it, from the sum payable to the seller of such gem and at the time such sum is paid to the seller.
2.5 Service fees and contract payments (Sec 85
Any person making the following payments is to withhold tax at 5% on amounts exceeding Rs. 50,000 per month from the following service fees with a source in Sri Lanka to a resident individual who is not an employee of the payer –
nfor teaching, lecturing, examining, invigilating or supervising an examination;
nas a commission or brokerage to a resident insurance, sales or canvassing agent;
nas an endorsement fee;
nin relation to the supply of any article on a contract basis through tender or quotation;
nfor such other matters as may be prescribed by regulation;
The Minister has by gazette extraordinary number 2064/51 dated 1st April 2018, set out the following services under “other matters” above. Accordingly, WHT would apply on the following services:
any service provided in the capacity of independent service providers such as doctors, engineers, accountants, lawyers, software developers, researchers, academics, or any other similar service ;
any service of construction work, security service, janitorial service, consultation work of any kind, organising of events, catering, designers, dress makers, tour guidance, entertainment, agency functions or any similar services or connected work where such services are provided under an agreement or otherwise;
any management service;
any type of vocational services provided as an independent service provider.
However, the WHT on investment returns, service fees and contract fees will not apply in certain instances set out in the law such as where the payments made by individuals, unless made in conducting a business, payments are exempt amounts etc. In the case of service fees paid to individuals, if the recipient is registered for ESC, a WHT direction can be obtained from the IRD.
nService fees/insurance premiums to non-residents
Any person paying a service fee or an insurance premium with a source in Sri Lanka to a non-resident person is to withhold 14% on such payment. There is also a 2% prescribed in certain telecommunication and transportation service payments made to a non-resident.
Withholding Tax payments (S.86)
Payments in respect of sums withheld must be remitted monthly within 15 days after the end of the each calendar month to the CGIR.
Consequences of
non-compliance
returns (S.86) filing:
Annually within 30 days from the end of the year of assessment (i.e. 31 March) including particulars such as payments made during the period that are subject to withholding, the name, address and tax identification number of the withholdee, tax withheld from each payment; and any other information that the Commissioner-General may specify
Withholding certificates (S.87)
A withholding agent is required to furnish to the withholdee a withholding certificate in due time and in the form specified which sets out the amount of payments made to the withholdee during the period and tax withheld by the withholding agent from those payments.
[The writer serves as the Director – Tax Services of BDO Partners and Heads the firm’s Tax Practice. She is a Chartered Accountant, an Associate Member of the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (UK), Member of the Chartered Institute for Securities and Investment (UK) and a Chartered Global Management Accountant.]